Theory
- WiFi refers to wireless local area network (WLAN) works based on IEEE 802.11 standard. It is a widely used technology for wireless communication across a radio channel.
- Personal computers, smartphones, video game console, etc. use WiFi to connect to the internet via a wireless network access point.
- Every network card has a physical static address known as MAC address.This address is unique, and the card manufacturer assigns it.
- This address is used between devices to identify each other and to transfer packets to the right place. Each packet has a source MAC and adestination MAC.
WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. Introduced as part of the original 802.11 standards ratified in 1997, its intention was to provide data confidentiality comparable to that of a traditional wired network.
A Standard 64-bit WEP uses a 40-bit key (also known as WEP-40), which is concatenated with a 24-bit initialization vector (IV) to form the RC4 key used for encryption.
RC4 is a stream cipher; the same traffic key must never be used twice. The purpose of an IV, which is transmitted as plain text, is to prevent any repetition, but a 24-bit IV is not long enough to ensure this on a busy network. The way the IV was used also opened WEP to a related key attack.
WPA
WPA stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access and is a security technology for Wi-Fi networks. It was developed in response to the weaknesses of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and therefore improves on WEP's authentication and encryption features.
WPA provides stronger encryption than WEP through use of either of two standard technologies: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). WPA also includes built-in authentication support that WEP does not offer. Some implementations of WPA allow for WEP clients to connect to the network too, but the security is then reduced to WEP-levels for all connected devices.
WPA includes support for authentication serves called Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service servers (RADIUS) servers. After connecting to a WPA network Once a device successfully connects to a WPA network. Devices make a four-way handshake with the access point to generate security keys.
When TKIP encryption is used, a message integrity code (MIC) is included to make sure that the data is not being spoofed. It replaces WEP's weaker packet guarantee called cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
WPA2
Short for Wi-Fi Protected Access 2, WPA2 is the security method added to WPA for wireless networks that provide stronger data protection and network access control. It provides enterprise and consumer Wi-Fi users with a high level of assurance that only authorized users can access their wireless networks. Based on the IEEE 802.11 i standard, WPA2 provides government grade security by implementing the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) FIPS 140-2 compliant AES encryption algorithm and 802.lx-based authentication.
There are two versions of WPA2: WPA2-Personal, and WPA2- Enterprise. WPA2-Personal protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up password. WPA2-Enterprise verifies network users through a server. WPA2 is backward compatible with WPA.
WPA3
WPA3 is the next generation of Wi-Fi security and provides cutting-edge security protocols to the market. Building on the widespread success and adoption of Wi-Fi CERTIFIED WPA2™, WPA3 adds new features to simplify Wi-Fi security, enable more robust authentication, deliver increased cryptographic strength for highly sensitive data markets, and maintain resiliency of mission-critical networks. All WPA3 networks
• Use the latest security methods
• Disallow outdated legacy protocols
• Require use of Protected Management Frames (PMF)
Since Wi-Fi networks differ in usage purpose and security needs, WPA3 includes additional capabilities specifically for personal and enterprise networks. Users of WPA3-Personal receive increased protection from password guessing attempts, while WPA3-Enterprise users can now take advantage of higher grade security protocols for sensitive data networks.
WPA3 which retains interoperability with WPA2™ devices is currently an optional certification for Wi-Fi CERTIFIED devices. It will become required over time as market adoption grows
WPA3-Personal
WPA3-Personal brings better protections to individual users by providing more robust password-based authentication, even when users choose passwords that fall short of typical complexity recommendations. This capability is enabled through Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE), which replaces Pre-shared Key (PSK) and WPA2-Personal. The technology is resistant to offline dictionary attacks where an adversary attempts to determine a network password by trying possible passwords without further network interaction.
• Natural password selection: Allows users to choose passwords that are easier to remember
• Ease of use: Delivers enhanced protections with no change to the way users connect to a network
• Forward secrecy: Protects data traffic even if a password is compromised after the data was transmitted
WPA3-Enterprise
WPA3-Enterprise. WPA3-Enterprise builds upon WPA2 and ensures the Enterprise, governments, and financial institutions have greater security with consistent application of security protocols across the network.
WPA3-Enterprise also offers an optional mode using 192-bit minimum-strength security protocols and cryptographic tools to better protect sensitive data :
• Authenticated encryption : 256-bit Galois/Counter Mode Protocol (GCMP-256)
• Key derivation and confirmation :384-bit Hashed Message Authentication Mode (HMAC) with Secure Hash Algorithm (HMAC• SHA384)
• Key establishment and authentication :Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH)exchange and Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) using a 384-bit elliptic curve
• Robust management frame protection : 256-bit Broadcast/Multicast Integrity Protocol Galois Message Authentication Code (BIP-GMAC-256)
The 192-bit security mode offered by WPA3-Enterprise ensures the right combination of cryptographic tools are used and sets a consistent baseline of security within a WPA3 network.
Types of Wireless Antennas :
Directional Antenna is used to broadcast and obtain radio waves from a single direction.
Omnidirectional Antenna provides a 360-degree horizontal radiation pattern. It is used in wireless base stations.
Parabolic Grid Antenna is based on the principle of a satellite dish, but it does not have a solid backing. They can pick up WiFi signals ten miles or more.
Yagi Antenna is a unidirectional antenna commonly used in communications for a frequency band of 10 MHz to VHF and UHF.
Dipole Antenna is a bidirectional antenna, used to support client connections rather than site-to-site applications.
Finding Open WiFi Networks
War Walking - Attackers walk around with WiFi-enabled laptops to detect open wireless networks.
War Chalking - A method used to draw symbols in public places to advertise open WiFi networks.
War Flying - In this technique, attackers use drones to detect open wireless networks.
War Driving - Attackers drive around with WiFi-enabled laptops todetect open wireless networks.
Aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng includes a set of tools to perform WiFi network hacking.
Monitoring : Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third-party tools.
Attacking : Replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points and others via packet injection.
Testing : Hecking WiFi cards and driver capabilities (capture and injection).
Cracking : WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2).
Airmon-ng
This script can be used to enable monitor mode on wireless interfaces. It may also be used to go back from monitor mode to managed mode. Entering the airmon-ng command without parameters will show the interfaces status.
Airodump-ng
Airodump-ng is used for packet capturing of raw 802.11 frames and is particularly suitable for collecting WEP IVs (Initialization Vector) for the intent of using them with aircrack-ng. If you have a GPS receiver connected to the computer, airodump-ng is capable of logging the coordinates of the found access points.
Additionally, airodump-ng writes out several files containing the details of all access points and clients seen.
Terminology
Bssid = Mac Address of The Access Point
Essid = Name of The Access Point
Ch = Channel Number of Access Point
Data = Data Packets Transferred
Beacons = Advertisement Packets Sent by Access Point
Pwr = Signal Strength of Access Point
Auth = Encryption Used by The Access Point
Cipher = Encryption Cipher Used by The Access Point
Aireplay-ng
Aireplay-ng is used to inject frames. The primary function is to generate traffic for the later use in aircrack-ng for cracking the WEP and WPA-PSK keys.
There are different attacks which can cause de-authentications to capture WPA handshake data, fake authentications, Interactive packet replay, hand• crafted ARP request injection and ARP-request reinjection. With the packet forge-ng tool, it's possible to create arbitrary frames. Most drivers need to be patched to be able to inject.
Airbase-ng
Airbase-ng is a multi-purpose tool aimed at attacking clients as opposed to the Access Point (AP) itself. Since it is so versatile and flexible, summarizing it is a challenge. Here are some of the feature highlights :
• Implements the Caffe Latte WEP client attack
• Implements the Hirte WEP client attack
• Ability to cause the WPA/WPA2 handshake to be captured
• Ability to act as an ad-hoc Access Point
• Ability to serve as a full Access Point
• Ability to filter by SSID or client MAC addresses
• Ability to manipulate and resend packets
• Ability to encrypt sent packets and decrypt received packets
WEP Cracking
It uses a stream cipher algorithm called RC4 where each packet is encrypted at the AP and is then decrypted at the client, WEP ensures that each packet has a unique keystream by using a random 24-bit Initialization Vector (IV), this IV is contained in the packets as plain text.
In a busy network we can collect more than two packets with the same IV, then we can use the aircrack-ng suite to determine WEP key.
Cracking WPA/WPA2 Encryption
Capturing WPA packets is not useful as they do not contain any info that can be used to crack the key. The only packet that contains info that helps us crack the password is the handshake packets.
Every time a client connects to that AP a four-way handshake occurs between the client and the AP. By capturing the handshake, we can use aircrack to launch a word list attack against the handshake to determine the key.
To crack a WPA/WPA2 AP with WPS disabled, we need two things :
1. Capture the Handshake
2. A wordlist
Cracking the WPA Key using a Wordlist
Use aircrack-ng to crack the key. It performs the job by combining each password in the wordlist with AP names (Essid) to compute a PMK (Pairwise Master Key) using the pbkdf2 algorithm; the PMK is then compared to the handshake file. Create wordlist using crunch tool to crack the WPA key
Exploiting WPS Feature
WPS is a feature that allows users to connect to WPS enabled networks easily, using a WPS button or only by clicking on WPS functionality. Authentication is done using an eight-digit long pin, this means that there is a relatively small number of pin combination and using brute force we can guess the pin in less than 10 hours. Tools like wifite or reaver can automate this process and recover the WPA key from that pin.
Note : This flaw is in the WPS feature and not in WPA/WPA2. However, it allows us to crack any WPA/WPA2 AP without using a wordlist and without any clients.
Cracking WiFi Passwords (Summary)
Bluetooth hacking :
Attackers take advantage of Bluetooth to perform various types of attacks. They exploit vulnerabilities in Bluetooth stack implementation to gain access to sensitive data in Bluetooth enabled devices and networks. Attackers gain sensitive information by hacking a Bluetooth enabled device from another Bluetooth enabled device.
Bluetooth attacks - Btlejacking, Bluesmacking, Bluejacking, Bluesnarfing, Bluesniff, and Blueprinting.
Countermeasures
- Do not use WEP encryption, as it is easy to crack.
- Use WPA2 with a complex password, make sure the password contains small letters, capital letters, symbols and numbers
- Ensure that the WPS feature is disabled as it can be used to crack your complex WPA2 key by brute-forcing the easy WPS pin.
- Enable MAC address filtering on access point or router.
- Set default router access password and enable firewall protection.
Practicals
Practical 1 : Cracking WEP Wi-Fi passwords.
Practical 1 : Cracking WEP Wi-Fi passwords.
Description : In this practical you will learn how to set up your system for performing WiFi hacking and different terminology in WiFi hacking. WEP is an old encryption technique used in WIFI' s, it is more vulnerable to exploitation, in this practical you will learn how to crack WiFi that are using WEP encryption technique.
Prerequisites : Air-crack suite installed in your system and external WiFi adapter if you are trying to perform WiFi attacks using a virtual machine.
Keywords :
• BSSID - Target Access Point MAC address
• CH - Channel Number of Target AP
• ESSID - Target Access Point Name
• Data - The amount of data packets sent or received by Target AP
• Beacons - The number of advertisement packets sent by Target AP
• ENC - Type of wireless encryption used for communication purpose.
• Cipher - Type of Algorithm used for encryption.
• Auth - Type of Authentication.
• Clients or Station-> The user MAC address connected to an AP.
Step 1 : Open a terminal and execute iwconfig to identify available network interfaces.
Step 2 : Start Wi-Fi interface on monitor mode
• syntax: airmon-ng start <Wi-Fi interface name>
Step 3 : To display the list of surrounded Wi-Fi networks, execute the following command.
• Syntax : airodump-ng <Wi-Fi monitoring interface>
Step 4 : To crack WEP Protected Wi-Fi network, capture a minimum of 20000 data packets. Execute the following command to start packet capturing.
• Syntax : airodump-ng --bssid <target AP mac> --essid <target AP name>
• channel <target channelnumber> --write <filename> <wifi monitormode name>
Step 6 : To crack WEP password, execute following command
• Syntax : aircrack-ng <filename-01.cap>
Practical 2 : Cracking WPA/WPA2 passwords using
Dictionary Attack.
Description : In this practical you will learn how to crack WiFi password for the WiFi that uses WPA/WPA2 encryption technique, by capturing the handshake and providing a wordlist.
Step 1 : Open a terminal and execute iwconfig to identify available network interfaces.
Description : In this practical you will learn how to crack WiFi password for the WiFi that uses WPA/WPA2 encryption technique, by capturing the handshake and providing a wordlist.
Step 1 : Open a terminal and execute iwconfig to identify available network interfaces.
Step 2 : Start Wi-Fi interface on monitor mode
• syntax: airmon-ng start <Wi-Fi interface name>
Step 3 : To display the list of surrounded Wi-Fi networks, execute the following command.
• Syntax : airodump-ng <Wi-Fi monitoring interface>
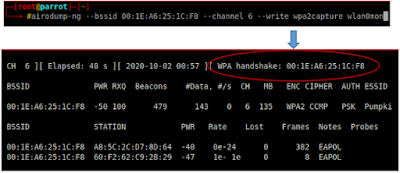
Step 4 : Select an access point (WPA/WPA2) BSSID and run airodump command to start capturing packets. We need to capture handshake packet to crack passwords of WPA/WPA2 protected networks
• Syntax : airodump-ng --bssid <target AP mac> --essid <target AP name>
-• channel <target channel number> --write <filename> <wifi monitormode name>
Step 5 : We must wait until a client connects to the access point to capture WPA handshake (As shown in the top right comer of the above image). If there is no client connected then we need to perform a deauthentication attack by executing the following command to capture a handshake packet.
• Syntax : aireplay-ng -0 0 -a <AP mac Address> -c <Station Mac address>
•-e <essid> <wifi monitormode name>
Step 6 : After capturing handshake, execute aircrack command to perform dictionary attack using default wordlist rockyou. txt or a custom build wordlist based on information gathering performed on target.
• Syntax : aircrack-ng <filename-01.ivs> -w <wordlist file path>
Download PDF : Google Drive
Telegram Channel : Link
Tags
Ethical-Hacking